Part:BBa_K136016:Experience
User Reviews
UFSCar-Brasil Team [http://2015.igem.org/Team:UFSCar-Brasil.html]
Experiences With This Constitutive GFP Generator Device Under Different Stress Conditions
This part was introduced also as BBa_K1620006 by our team.
Contents
Usage and Biology
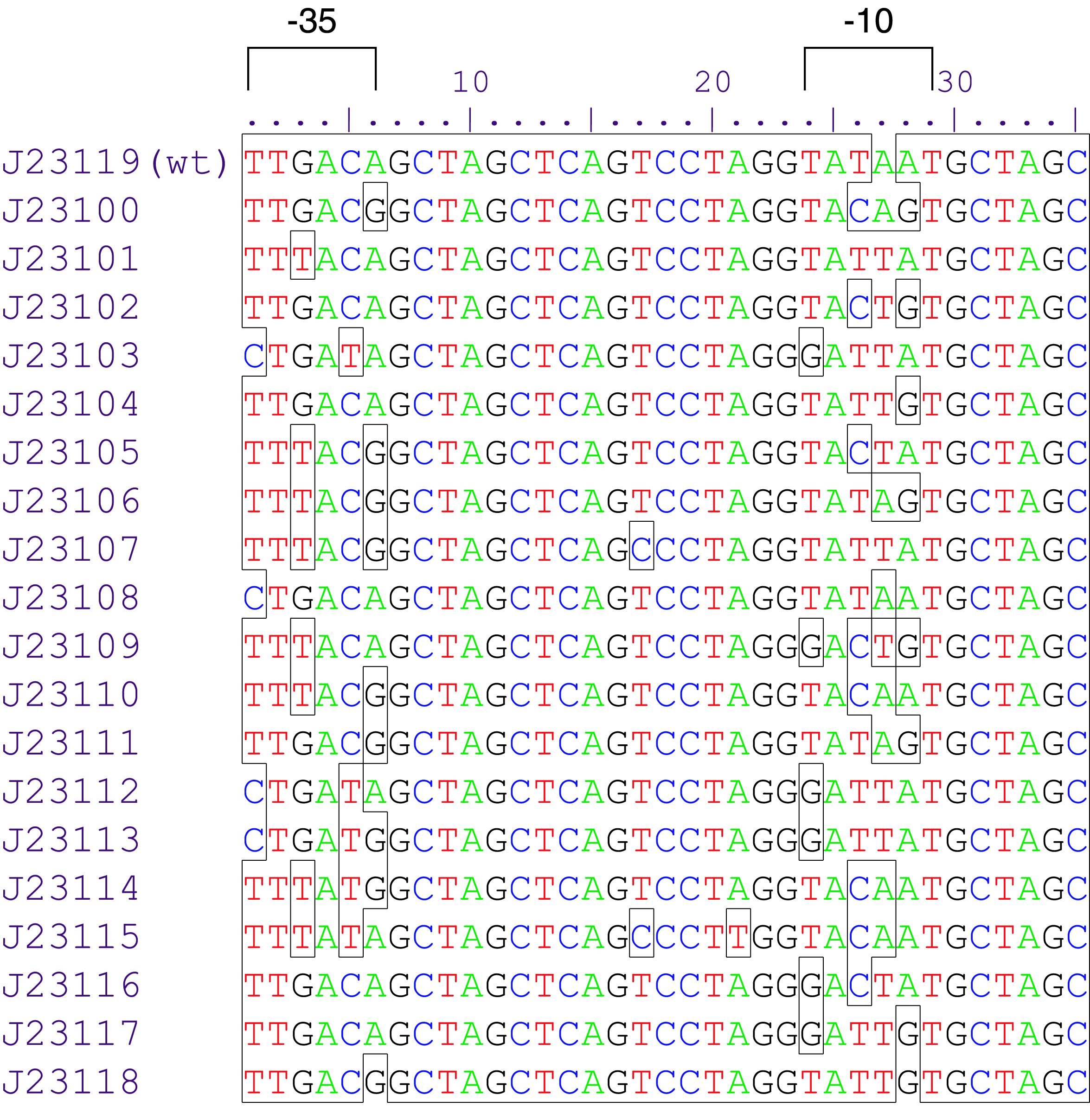
The part BBa_J23101 is a promoter from a synthetic family of constitutive promoter parts isolated from a small combinatorial library (Figure 1). J23101 is 1791 fold the original promoter J23112, and the third more efficient element in the list. Reported activities of this promoters were given as the relative fluorescence of plasmid pSB1C3 carrying mRFP gene in strain DH5alpha grown in Lysogenic Broth media to saturation. This device generates permanently and a low rate GFP reporter, since the fusion of J23101 with biobrick BBa_E0840. It is usefull for cell marker and promoter strength tests. This composite presents NheI and AvrII restriction sites within these promoter parts making it a scaffold for further modification.
GFP expression tests
Test of cold shock
The E. coli DH5α clone carrying the construct pJ23101::gfp was grown in 100 mL of lysogenic broth containing chloramphenicol as previously referred (LB plus chloram) in a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask under 200 rpm at 37°C. After culture reach optical density of 0.5, a sample of 5 mL was collected for protein analysis. The remaining broth was transferred to a 4°C chamber without agitation for 16 h. The cells were harvested by centrifugation. The protein analysis was carried out through a SDS-PAGE, using normalized samples, and a GFP fluorescence reading in black Elisa plates using Viktor (Perkin-Elmer).

Test of osmotic shock
The strain E. coli DH5α_pJ23101::gfp was grown under soft conditions (Lysogenic Broth Chloramphenicol supplemented, 37°C – 200 rpm) overnight, and cells were harvested from 2 mL cultures by centrifugation (4,000 rpm – 4°C, 6 min). These cells were resuspended in 1 mL of Lysogenic broth containing the propper antibiotic and different concentrations of PEG 6000 ranging from 0 to 30% (in 2% steps until 20%). The 96 deep well plates were incubated at 37°C for 4 h, under 200 rpm. Finally, the cells were harvested by centrifugation as described before and the lysis was carried out after resuspension of cells in 180 μL of lysis buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, 50 mM NaH2PO4, pH 7.5) with 20 μL volume of neutral detergent based lysis solution 10X (10mM EDTA, 10 mg/mL Lisozyme, 10% Triton X-100, 100 mM Tris-HCl – pH 8) at room temperature for 15 min with careful agitation at each 5 min. After lysis, the cell debris was precipitated by long time centrifugation (4,000 rpm – 4°C, 45 min) and the supernatant was collected to a 96 well Elisa black plate. The GFP was measured in Viktor (Perkin Elmer) plate fluorometer. Soluble and insoluble fractions were used in a SDS-PAGE.

Test of Starving
Cells carrying pJ23101::gfp were grown overnight in Lysogenic broth supplemented with chloramphenicol at 37°C under 200 rpm. Then, the cells were harvested by centrifugation and washed with sterile Tris-Saline (10mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl). Cells were resuspended in two different media: Lysogenic broth and Poor Medium (2 g/L Ammonium Sulfate, 13.6 g/L Monobasic Potassium Phosphate, 25 mg Lysogenic Broth (HiMedia), 10 μg/mL Cloramphenicol, filter sterilized), at equal optical densities. The cultures were incubated at 37°C under 200 rpm for 4h. Samples were collected at each hour and in the initial times. Finally, the cells were lysed as to the test of osmotic shock. A SDS-PAGE was used to compare the crude protein extracts, and the fluorometer was used to quantify the total produced GFP (as previously referred).

Conclusions
As observed all stress situations are capable to reduce the overall GFP production of this device. In this sense, the GFP production could be taken, using this system, as a control of any adverse situation that cell could be observe. Furthermore, the constitutive character helps the detection of the cells, turning this device extremelly usefull for detections or positive clonning.
